Ch 10: Emotion and Motivation

What makes us behave as we do? Is there a biological basis to explain the feelings we experience? How universal are emotions?
In this chapter, we will explore issues relating to both emotion and motivation. We will begin with a brief discussion of several theories that have been proposed to explain motivation and why we engage in a given behavior. You will learn about the physiological needs that drive some human behaviors, as well as the importance of our social experiences in influencing our actions.
This chapter will close with a discussion of emotion. You will learn about several theories that have been proposed to explain how emotion occurs, the biological underpinnings of emotion, and the universality of emotions.
Motivation
 Motivation to engage in a given behavior can come from internal and/or external factors. There are multiple theories have been put forward regarding motivation. In this section, you’ll learn about these theories as well as the famous work of Abraham Maslow and his hierarchy of needs.
Motivation to engage in a given behavior can come from internal and/or external factors. There are multiple theories have been put forward regarding motivation. In this section, you’ll learn about these theories as well as the famous work of Abraham Maslow and his hierarchy of needs.
Motivation
- Illustrate intrinsic and extrinsic motivation
- Describe basic theories of motivation, including concepts such as instincts, drive reduction, and self-efficacy
- Explain the basic concepts associated with Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
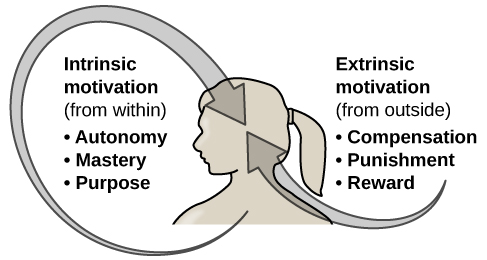
Why do we do the things we do? What motivations underlie our behaviors? Motivation describes the wants or needs that direct behavior toward a goal. In addition to biological motives, motivations can be intrinsic (arising from internal factors) or extrinsic (arising from external factors) (Figure 2). Intrinsically motivated behaviors are performed because of the sense of personal satisfaction that they bring, while extrinsically motivated behaviors are performed in order to receive something from others.
Think about why you are currently in college. Are you here because you enjoy learning and want to pursue an education to make yourself a more well-rounded individual? If so, then you are intrinsically motivated. However, if you are here because you want to get a college degree to make yourself more marketable for a high-paying career or to satisfy the demands of your parents, then your motivation is more extrinsic in nature.
Try It
In reality, our motivations are often a mix of both intrinsic and extrinsic factors, but the nature of the mix of these factors might change over time (often in ways that seem counter-intuitive). There is an old adage: “Choose a job that you love, and you will never have to work a day in your life,” meaning that if you enjoy your occupation, work doesn’t seem like . . . well, work. Some research suggests that this isn’t necessarily the case (Daniel & Esser, 1980; Deci, 1972; Deci, Koestner, & Ryan, 1999). According to this research, receiving some sort of extrinsic reinforcement (i.e., getting paid) for engaging in behaviors that we enjoy leads to those behaviors being thought of as work no longer providing that same enjoyment. As a result, we might spend less time engaging in these reclassified behaviors in the absence of any extrinsic reinforcement. For example, Odessa loves baking, so in her free time, she bakes for fun. Oftentimes, after stocking shelves at her grocery store job, she often whips up pastries in the evenings because she enjoys baking. When a coworker in the store’s bakery department leaves his job, Odessa applies for his position and gets transferred to the bakery department. Although she enjoys what she does in her new job, after a few months, she no longer has much desire to concoct tasty treats in her free time. Baking has become work in a way that changes her motivation to do it (Figure 3). What Odessa has experienced is called the overjustification effect—intrinsic motivation is diminished when extrinsic motivation is given. This can lead to extinguishing the intrinsic motivation and creating a dependence on extrinsic rewards for continued performance (Deci et al., 1999).

Other studies suggest that intrinsic motivation may not be so vulnerable to the effects of extrinsic reinforcements, and in fact, reinforcements such as verbal praise might actually increase intrinsic motivation (Arnold, 1976; Cameron & Pierce, 1994). In that case, Odessa’s motivation to bake in her free time might remain high if, for example, customers regularly compliment her baking or cake decorating skills.
These apparent discrepancies in the researchers’ findings may be understood by considering several factors. For one, physical reinforcement (such as money) and verbal reinforcement (such as praise) may affect an individual in very different ways. In fact, tangible rewards (i.e., money) tend to have more negative effects on intrinsic motivation than do intangible rewards (i.e., praise). Furthermore, the expectation of the extrinsic motivator by an individual is crucial: If the person expects to receive an extrinsic reward, then intrinsic motivation for the task tends to be reduced. If, however, there is no such expectation, and the extrinsic motivation is presented as a surprise, then intrinsic motivation for the task tends to persist (Deci et al., 1999).
In educational settings, students are more likely to experience intrinsic motivation to learn when they feel a sense of belonging and respect in the classroom. This internalization can be enhanced if the evaluative aspects of the classroom are de-emphasized and if students feel that they exercise some control over the learning environment. Furthermore, providing students with activities that are challenging, yet doable, along with a rationale for engaging in various learning activities can enhance intrinsic motivation for those tasks (Niemiec & Ryan, 2009). Consider Hakim, a first-year law student with two courses this semester: Family Law and Criminal Law. The Family Law professor has a rather intimidating classroom: He likes to put students on the spot with tough questions, which often leaves students feeling belittled or embarrassed. Grades are based exclusively on quizzes and exams, and the instructor posts results of each test on the classroom door. In contrast, the Criminal Law professor facilitates classroom discussions and respectful debates in small groups. The majority of the course grade is not exam-based, but centers on a student-designed research project on a crime issue of the student’s choice. Research suggests that Hakim will be less intrinsically motivated in his Family Law course, where students are intimidated in the classroom setting, and there is an emphasis on teacher-driven evaluations. Hakim is likely to experience a higher level of intrinsic motivation in his Criminal Law course, where the class setting encourages inclusive collaboration and a respect for ideas, and where students have more influence over their learning activities.
Try It

Another early theory of motivation proposed that the maintenance of homeostasis is particularly important in directing behavior. You may recall from your earlier reading that homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a balance, or optimal level, within a biological system. In a body system, a control center (which is often part of the brain) receives input from receptors (which are often complexes of neurons). The control center directs effectors (which may be other neurons) to correct any imbalance detected by the control center.
According to the drive theory of motivation, deviations from homeostasis create physiological needs. These needs result in psychological drive states that direct behavior to meet the need and, ultimately, bring the system back to homeostasis. For example, if it’s been a while since you ate, your blood sugar levels will drop below normal. This low blood sugar will induce a physiological need and a corresponding drive state (i.e., hunger) that will direct you to seek out and consume food (Figure 2). Eating will eliminate the hunger, and, ultimately, your blood sugar levels will return to normal. Interestingly, drive theory also emphasizes the role that habits play in the type of behavioral response in which we engage. A habit is a pattern of behavior in which we regularly engage. Once we have engaged in a behavior that successfully reduces a drive, we are more likely to engage in that behavior whenever faced with that drive in the future (Graham & Weiner, 1996).

Extensions of drive theory take into account levels of arousal as potential motivators. Just as drive theory aims to return the body to homeostasis, arousal theory aims to find the optimal level of arousal. If we are underaroused, we become bored and will seek out some sort of stimulation. On the other hand, if we are overaroused, we will engage in behaviors to reduce our arousal (Berlyne, 1960). Most students have experienced this need to maintain optimal levels of arousal over the course of their academic career. Think about how much stress students experience toward the end of spring semester. They feel overwhelmed with seemingly endless exams, papers, and major assignments that must be completed on time. They probably yearn for the rest and relaxation that awaits them over the extended summer break. However, once they finish the semester, it doesn’t take too long before they begin to feel bored. Generally, by the time the next semester is beginning in the fall, many students are quite happy to return to school. This is an example of how arousal theory works.

So what is the optimal level of arousal? What level leads to the best performance? Research shows that moderate arousal is generally best; when arousal is very high or very low, performance tends to suffer (Yerkes & Dodson, 1908). Think of your arousal level regarding taking an exam for this class. If your level is very low, such as boredom and apathy, your performance will likely suffer. Similarly, a very high level, such as extreme anxiety, can be paralyzing and hinder performance. Consider the example of a softball team facing a tournament. They are favored to win their first game by a large margin, so they go into the game with a lower level of arousal and get beat by a less skilled team.
But optimal arousal level is more complex than a simple answer that the middle level is always best. Researchers Robert Yerkes (pronounced “Yerk-EES”) and John Dodson discovered that the optimal arousal level depends on the complexity and difficulty of the task to be performed (Figure 4). This relationship is known as Yerkes-Dodson law, which holds that a simple task is performed best when arousal levels are relatively high and complex tasks are best performed when arousal levels are lower.

Self-efficacy and Social Motives
Self-efficacy is an individual’s belief in her own capability to complete a task, which may include a previous successful completion of the exact task or a similar task. Albert Bandura (1994) theorized that an individual’s sense of self-efficacy plays a pivotal role in motivating behavior. Bandura argues that motivation derives from expectations that we have about the consequences of our behaviors, and ultimately, it is the appreciation of our capacity to engage in a given behavior that will determine what we do and the future goals that we set for ourselves. For example, if you have a sincere belief in your ability to achieve at the highest level, you are more likely to take on challenging tasks and to not let setbacks dissuade you from seeing the task through to the end.
A number of theorists have focused their research on understanding social motives (McAdams & Constantian, 1983; McClelland & Liberman, 1949; Murray et al., 1938). Among the motives they describe are needs for achievement, affiliation, and intimacy. It is the need for achievement that drives accomplishment and performance. The need for affiliation encourages positive interactions with others, and the need for intimacy causes us to seek deep, meaningful relationships. Henry Murray et al. (1938) categorized these needs into domains. For example, the need for achievement and recognition falls under the domain of ambition. Dominance and aggression were recognized as needs under the domain of human power, and play was a recognized need in the domain of interpersonal affection.
Link to Learning
Watch this video from Dan Pink’s Ted talk on “The surprising truth about what motivates us.” Think about what things motivate you, and how you anticipate that you might respond to the types of incentives explained in the talk.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
While most theories of motivation relate to basic biological drives, individual characteristics, or social contexts, Abraham Maslow (1943) proposed a hierarchy of needs that spans the spectrum of motives ranging from the biological to the individual to the social. These needs are often depicted as a pyramid (Figure 4).

At the base of the pyramid are all of the physiological needs that are necessary for survival. These are followed by basic needs for security and safety, the need to be loved and to have a sense of belonging, and the need to have self-worth and confidence. The top tier of the pyramid is self-actualization, which is a need that essentially equates to achieving one’s full potential, and it can only be realized when needs lower on the pyramid have been met. To Maslow and humanistic theorists, self-actualization reflects the humanistic emphasis on positive aspects of human nature. Maslow suggested that this is an ongoing, life-long process and that only a small percentage of people actually achieve a self-actualized state (Francis & Kritsonis, 2006; Maslow, 1943).
According to Maslow (1943), one must satisfy lower-level needs before addressing those needs that occur higher in the pyramid. So, for example, if someone is struggling to find enough food to meet his nutritional requirements, it is quite unlikely that he would spend an inordinate amount of time thinking about whether others viewed him as a good person or not. Instead, all of his energies would be geared toward finding something to eat. However, it should be pointed out that Maslow’s theory has been criticized for its subjective nature and its inability to account for phenomena that occur in the real world (Leonard, 1982). Other research has more recently addressed that late in life, Maslow proposed a self-transcendence level above self-actualization—to represent striving for meaning and purpose beyond the concerns of oneself (Koltko-Rivera, 2006). For example, people sometimes make self-sacrifices in order to make a political statement or in an attempt to improve the conditions of others. Mohandas K. Gandhi, a world-renowned advocate for independence through nonviolent protest, on several occasions went on hunger strikes to protest a particular situation. People may starve themselves or otherwise put themselves in danger displaying higher-level motives beyond their own needs.
Link to Learning
Check out this interactive exercise that illustrates some of the important concepts in Maslow’s hierarchy of needs.
Review Maslow’s hierarchy of needs as well as the other theories of motivation in this Crash Course video.
Try It
Think It Over
- Can you think of recent examples of how Maslow’s hierarchy of needs might have affected your behavior in some way?
Try It
Emotion
As we move through our daily lives, we experience a variety of emotions (which we often call “feelings”). Emotions are subjective states of being that, physiologically speaking, involve physiological arousal, psychological appraisal and cognitive processes, subjective experiences, and expressive behavior. Emotions are often the driving force behind motivation (whether positive or negative) and are expressed and communicated through a wide range of behaviors, such as tone of voice and body language.
Our psychological appraisal of a situation is informed by our experiences, background, and culture. Therefore, different people may have different emotional experiences of similar situations. However, the ability to produce and recognize emotional facial expressions seems to be universal. That said, cultures differ in how often and under what circumstances it is “okay” to express various emotions, as well as how various expressions of emotions are interpreted.
Emotion
Learning Objectives
- Compare and contrast the the Cannon-Bard, James-Lange, Schachter-Singer two-factor, and other theories of emotion
- Describe the role that limbic structures play in emotional processing
- Classify and explain how emotions are recognized and expressed
Theories of Emotion
As we move through our daily lives, we experience a variety of emotions. An emotion is a subjective state of being that we often describe as our feelings. The words emotion and mood are sometimes used interchangeably, but psychologists use these words to refer to two different things. Typically, the word emotion indicates a subjective, affective state that is relatively intense and that occurs in response to something we experience (Figure 5). Emotions are often thought to be consciously experienced and intentional. Mood, on the other hand, refers to a prolonged, less intense, affective state that does not occur in response to something we experience. Mood states may not be consciously recognized and do not carry the intentionality that is associated with emotion (Beedie, Terry, Lane, & Devonport, 2011). Here we will focus on emotion, and you will learn more about mood in the chapter that covers psychological disorders.

We can be at the heights of joy or in the depths of despair or. We might feel angry when we are betrayed, fear when we are threatened, and surprised when something unexpected happens. This section will outline some of the most well-known theories explaining our emotional experience and provide insight into the biological bases of emotion. This section closes with a discussion of the ubiquitous nature of facial expressions of emotion and our abilities to recognize those expressions in others.

It is important to point out that Schachter and Singer believed that physiological arousal is very similar across the different types of emotions that we experience, and therefore, the cognitive appraisal of the situation is critical to the actual emotion experienced. In fact, it might be possible to misattribute arousal to an emotional experience if the circumstances were right (Schachter & Singer, 1962).
To test their idea, Schachter and Singer performed a clever experiment. Male participants were randomly assigned to one of several groups. Some of the participants received injections of epinephrine that caused bodily changes that mimicked the fight-or-flight response of the sympathetic nervous system; however, only some of these men were told to expect these reactions as side effects of the injection. The other men that received injections of epinephrine were told either that the injection would have no side effects or that it would result in a side effect unrelated to a sympathetic response, such as itching feet or headache. After receiving these injections, participants waited in a room with someone else they thought was another subject in the research project. In reality, the other person was a confederate of the researcher. The confederate engaged in scripted displays of euphoric or angry behavior (Schachter & Singer, 1962).
When those subjects who were told that they should expect to feel symptoms of physiological arousal were asked about any emotional changes that they had experienced related to either euphoria or anger (depending on how their confederate behaved), they reported none. However, the men who weren’t expecting physiological arousal as a function of the injection were more likely to report that they experienced euphoria or anger as a function of their assigned confederate’s behavior. While everyone that received an injection of epinephrine experienced the same physiological arousal, only those who were not expecting the arousal used context to interpret the arousal as a change in emotional state (Schachter & Singer, 1962).
Strong emotional responses are associated with strong physiological arousal. This has led some to suggest that the signs of physiological arousal, which include increased heart rate, respiration rate, and sweating, might serve as a tool to determine whether someone is telling the truth or not. The assumption is that most of us would show signs of physiological arousal if we were being dishonest with someone. A polygraph, or lie detector test, measures the physiological arousal of an individual responding to a series of questions. Someone trained in reading these tests would look for answers to questions that are associated with increased levels of arousal as potential signs that the respondent may have been dishonest on those answers. While polygraphs are still commonly used, their validity and accuracy are highly questionable because there is no evidence that lying is associated with any particular pattern of physiological arousal (Saxe & Ben-Shakhar, 1999).
Try It
The relationship between our experiencing of emotions and our cognitive processing of them, and the order in which these occur, remains a topic of research and debate. Lazarus (1991) developed the cognitive-mediational theory that asserts our emotions are determined by our appraisal of the stimulus. This appraisal mediates between the stimulus and the emotional response, and it is immediate and often unconscious. In contrast to the Schachter-Singer model, the appraisal precedes a cognitive label. You will learn more about Lazarus’s appraisal concept when you study stress, health, and lifestyle.
Two other prominent views arise from the work of Robert Zajonc and Joseph LeDoux. Zajonc asserted that some emotions occur separately from or prior to our cognitive interpretation of them, such as feeling fear in response to an unexpected loud sound (Zajonc, 1998). He also believed in what we might casually refer to as a gut feeling—that we can experience an instantaneous and unexplainable like or dislike for someone or something (Zajonc, 1980). LeDoux also views some emotions as requiring no cognition: some emotions completely bypass contextual interpretation. His research into the neuroscience of emotion has demonstrated the amygdala’s primary role in fear (Cunha, Monfils, & LeDoux, 2010; LeDoux 1996, 2002). A fear stimulus is processed by the brain through one of two paths: from the thalamus (where it is perceived) directly to the amygdala or from the thalamus through the cortex and then to the amygdala. The first path is quick, while the second enables more processing about details of the stimulus. In the following section, we will look more closely at the neuroscience of emotional response.
Dig Deeper: Psychology in Music
Watch It
Review the theories of emotion in the following Crash Course Psychology video.
Try It
Think It Over
Think about times in your life when you have been absolutely elated (e.g., perhaps your school’s basketball team just won a closely contested ballgame for the national championship) and very fearful (e.g., you are about to give a speech in your public speaking class to a roomful of 100 strangers). How would you describe how your arousal manifested itself physically? Were there marked differences in physiological arousal associated with each emotional state?
Try It
The Biology of Emotions
Earlier, you learned about the limbic system, which is the area of the brain involved in emotion and memory (Figure 7). The limbic system includes the hypothalamus, thalamus, amygdala, and the hippocampus. The hypothalamus plays a role in the activation of the sympathetic nervous system that is a part of any given emotional reaction. The thalamus serves as a sensory relay center whose neurons project to both the amygdala and the higher cortical regions for further processing. The amygdala plays a role in processing emotional information and sending that information on to cortical structures (Fossati, 2012).The hippocampus integrates emotional experience with cognition (Femenía, Gómez-Galán, Lindskog, & Magara, 2012).

Link to Learning
Amygdala
The amygdala has received a great deal of attention from researchers interested in understanding the biological basis for emotions, especially fear and anxiety (Blackford & Pine, 2012; Goosens & Maren, 2002; Maren, Phan, & Liberzon, 2013). The amygdala is composed of various subnuclei, including the basolateral complex and the central nucleus (Figure 8). The basolateral complex has dense connections with a variety of sensory areas of the brain. It is critical for classical conditioning and for attaching emotional value to learning processes and memory. The central nucleus plays a role in attention, and it has connections with the hypothalamus and various brainstem areas to regulate the autonomic nervous and endocrine systems’ activity (Pessoa, 2010).

Animal research has demonstrated that there is increased activation of the amygdala in rat pups that have odor cues paired with electrical shock when their mother is absent. This leads to an aversion to the odor cue that suggests the rats learned to fear the odor cue. Interestingly, when the mother was present, the rats actually showed a preference for the odor cue despite its association with an electrical shock. This preference was associated with no increases in amygdala activation. This suggests a differential effect on the amygdala by the context (the presence or absence of the mother) determined whether the pups learned to fear the odor or to be attracted to it (Moriceau & Sullivan, 2006).
Raineki, Cortés, Belnoue, and Sullivan (2012) demonstrated that, in rats, negative early life experiences could alter the function of the amygdala and result in adolescent patterns of behavior that mimic human mood disorders. In this study, rat pups received either abusive or normal treatment during postnatal days 8–12. There were two forms of abusive treatment. The first form of abusive treatment had an insufficient bedding condition. The mother rat had insufficient bedding material in her cage to build a proper nest that resulted in her spending more time away from her pups trying to construct a nest and less times nursing her pups. The second form of abusive treatment had an associative learning task that involved pairing odors and an electrical stimulus in the absence of the mother, as described above. The control group was in a cage with sufficient bedding and was left undisturbed with their mothers during the same time period. The rat pups that experienced abuse were much more likely to exhibit depressive-like symptoms during adolescence when compared to controls. These depressive-like behaviors were associated with increased activation of the amygdala.
Human research also suggests a relationship between the amygdala and psychological disorders of mood or anxiety. Changes in amygdala structure and function have been demonstrated in adolescents who are either at-risk or have been diagnosed with various mood and/or anxiety disorders (Miguel-Hidalgo, 2013; Qin et al., 2013). It has also been suggested that functional differences in the amygdala could serve as a biomarker to differentiate individuals suffering from bipolar disorder from those suffering from major depressive disorder (Fournier, Keener, Almeida, Kronhaus, & Phillips, 2013).
Hippocampus
As mentioned earlier, the hippocampus is also involved in emotional processing. Like the amygdala, research has demonstrated that hippocampal structure and function are linked to a variety of mood and anxiety disorders. Individuals suffering from posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) show marked reductions in the volume of several parts of the hippocampus, which may result from decreased levels of neurogenesis and dendritic branching (the generation of new neurons and the generation of new dendrites in existing neurons, respectively) (Wang et al., 2010). While it is impossible to make a causal claim with correlational research like this, studies have demonstrated behavioral improvements and hippocampal volume increases following either pharmacological or cognitive-behavioral therapy in individuals suffering from PTSD (Bremner & Vermetten, 2004; Levy-Gigi, Szabó, Kelemen, & Kéri, 2013).
Try It
Facial Expression and Recognition of Emotions
Culture can impact the way in which people display emotion. A cultural display rule is one of a collection of culturally specific standards that govern the types and frequencies of displays of emotions that are acceptable (Malatesta & Haviland, 1982). Therefore, people from varying cultural backgrounds can have very different cultural display rules of emotion. For example, research has shown that individuals from the United States express negative emotions like fear, anger, and disgust both alone and in the presence of others, while Japanese individuals only do so while alone (Matsumoto, 1990). Furthermore, individuals from cultures that tend to emphasize social cohesion are more likely to engage in suppression of emotional reaction so they can evaluate which response is most appropriate in a given context (Matsumoto, Yoo, & Nakagawa, 2008).
Other distinct cultural characteristics might be involved in emotionality. For instance, there may be gender differences involved in emotional processing. While research into gender differences in emotional display is equivocal, there is some evidence that men and women may differ in regulation of emotions (McRae, Ochsner, Mauss, Gabrieli, & Gross, 2008).

Does smiling make you happy? Or does being happy make you smile? The facial feedback hypothesis asserts that facial expressions are capable of influencing our emotions, meaning that smiling can make you feel happier (Buck, 1980; Soussignan, 2001; Strack, Martin, & Stepper, 1988). Recent research explored how Botox, which paralyzes facial muscles and limits facial expression, might affect emotion. Havas, Glenberg, Gutowski, Lucarelli, and Davidson (2010) discovered that depressed individuals reported less depression after paralysis of their frowning muscles with Botox injections.
Link to Learning
The television program Lie to Me was based off of the idea that people can learn to read facial microexpressions and detect when another person is telling a lie. Although many criticize the human ability to actually detect lies through visual cues, psychologist Paul Ekman has done extensive research on the human face and how to better read emotions through even the slighted facial movements.
Another way to spot lies is through language. Watch this TEDEd video to learn more.
Of course, emotion is not only displayed through facial expression. We also use the tone of our voices, various behaviors, and body language to communicate information about our emotional states. Body language is the expression of emotion in terms of body position or movement. Research suggests that we are quite sensitive to the emotional information communicated through body language, even if we’re not consciously aware of it (de Gelder, 2006; Tamietto et al., 2009).
Link to Learning
Connect the Concepts: Autism Spectrum Disorder and Expression of Emotions
Try It
Hunger and Eating
Eating is essential for survival, and it is no surprise that a drive like hunger exists to ensure that we seek out sustenance. While we will focus primarily on the physiological mechanisms that regulate hunger and eating, powerful social, cultural, and economic influences also play important roles. This section will explain the regulation of hunger, eating, and body weight, and we will discuss the adverse consequences of disordered eating.
Hunger and Eating
- Describe how hunger and eating are regulated
- Differentiate between levels of overweight and obesity and the associated health consequences
- Explain the health consequences resulting from anorexia and bulimia nervosa
While nearly two out of three US adults struggle with issues related to being overweight, a smaller, but significant, portion of the population has eating disorders that typically result in being normal weight or underweight. Often, these individuals are fearful of gaining weight. Individuals who suffer from bulimia nervosa and anorexia nervosa face many adverse health consequences (Mayo Clinic, 2012a, 2012b).
People suffering from bulimia nervosa engage in binge eating behavior that is followed by an attempt to compensate for the large amount of food consumed. Purging the food by inducing vomiting or through the use of laxatives are two common compensatory behaviors. Some affected individuals engage in excessive amounts of exercise to compensate for their binges. Bulimia is associated with many adverse health consequences that can include kidney failure, heart failure, and tooth decay. In addition, these individuals often suffer from anxiety and depression, and they are at an increased risk for substance abuse (Mayo Clinic, 2012b). The lifetime prevalence rate for bulimia nervosa is estimated at around 1% for women and less than 0.5% for men (Smink, van Hoeken, & Hoek, 2012).
As of the 2013 release of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual, fifth edition, binge eating disorder is a disorder recognized by the American Psychiatric Association (APA). Unlike with bulimia, eating binges are not followed by inappropriate behavior, such as purging, but they are followed by distress, including feelings of guilt and embarrassment. The resulting psychological distress distinguishes binge eating disorder from overeating (American Psychiatric Association [APA], 2013).
Anorexia nervosa is an eating disorder characterized by the maintenance of a body weight well below average through starvation and/or excessive exercise. Individuals suffering from anorexia nervosa often have a distorted body image, referenced in literature as a type of body dysmorphia, meaning that they view themselves as overweight even though they are not. Like bulimia nervosa, anorexia nervosa is associated with a number of significant negative health outcomes: bone loss, heart failure, kidney failure, amenorrhea (cessation of the menstrual period), reduced function of the gonads, and in extreme cases, death. Furthermore, there is an increased risk for a number of psychological problems, which include anxiety disorders, mood disorders, and substance abuse (Mayo Clinic, 2012a). Estimates of the prevalence of anorexia nervosa vary from study to study but generally range from just under one percent to just over four percent in women. Generally, prevalence rates are considerably lower for men (Smink et al., 2012).
Link to Learning
Watch this news story about an Italian advertising campaign to raise public awareness of anorexia nervosa.
While both anorexia and bulimia nervosa occur in men and women of many different cultures, Caucasian females from Western societies tend to be the most at-risk population. Recent research indicates that females between the ages of 15 and 19 are most at risk, and it has long been suspected that these eating disorders are culturally-bound phenomena that are related to messages of a thin ideal often portrayed in popular media and the fashion world (Figure 5) (Smink et al., 2012). While social factors play an important role in the development of eating disorders, there is also evidence that genetic factors may predispose people to these disorders (Collier & Treasure, 2004).

Watch It
Learn more about eating and body dysmorphic orders in the following Crash Course Psychology video.
Think It Over
- Think about popular television programs on the air right now. What do the women in these programs look like? What do the men look like? What kinds of messages do you think the media is sending about men and women in our society?
Physiological Mechanisms
There are a number of physiological mechanisms that serve as the basis for hunger. When our stomachs are empty, they contract, causing both hunger pangs and the secretion of chemical messages that travel to the brain to serve as a signal to initiate feeding behavior. When our blood glucose levels drop, the pancreas and liver generate a number of chemical signals that induce hunger (Konturek et al., 2003; Novin, Robinson, Culbreth, & Tordoff, 1985) and thus initiate feeding behavior.
For most people, once they have eaten, they feel satiation, or fullness and satisfaction, and their eating behavior stops. Like the initiation of eating, satiation is also regulated by several physiological mechanisms. As blood glucose levels increase, the pancreas and liver send signals to shut off hunger and eating (Drazen & Woods, 2003; Druce, Small, & Bloom, 2004; Greary, 1990). The food’s passage through the gastrointestinal tract also provides important satiety signals to the brain (Woods, 2004), and fat cells release leptin, a satiety hormone.
The various hunger and satiety signals that are involved in the regulation of eating are integrated in the brain. Research suggests that several areas of the hypothalamus and hindbrain are especially important sites where this integration occurs (Ahima & Antwi, 2008; Woods & D’Alessio, 2008). Ultimately, activity in the brain determines whether or not we engage in feeding behavior (Figure 1).

Metabolism and Body Weight
Our body weight is affected by a number of factors, including gene-environment interactions, and the number of calories we consume versus the number of calories we burn in daily activity. If our caloric intake exceeds our caloric use, our bodies store excess energy in the form of fat. If we consume fewer calories than we burn off, then stored fat will be converted to energy. Our energy expenditure is obviously affected by our levels of activity, but our body’s metabolic rate also comes into play. A person’s metabolic rate is the amount of energy that is expended in a given period of time, and there is tremendous individual variability in our metabolic rates. People with high rates of metabolism are able to burn off calories more easily than those with lower rates of metabolism.
We all experience fluctuations in our weight from time to time, but generally, most people’s weights fluctuate within a narrow margin, in the absence of extreme changes in diet and/or physical activity. This observation led some to propose a set-point theory of body weight regulation. The set-point theory asserts that each individual has an ideal body weight, or set point, which is resistant to change. This set-point is genetically predetermined and efforts to move our weight significantly from the set-point are resisted by compensatory changes in energy intake and/or expenditure (Speakman et al., 2011).
Some of the predictions generated from this particular theory have not received empirical support. For example, there are no changes in metabolic rate between individuals who had recently lost significant amounts of weight and a control group (Weinsier et al., 2000). In addition, the set-point theory fails to account for the influence of social and environmental factors in the regulation of body weight (Martin-Gronert & Ozanne, 2013; Speakman et al., 2011). Despite these limitations, set-point theory is still often used as a simple, intuitive explanation of how body weight is regulated.
Obesity
When someone weighs more than what is generally accepted as healthy for a given height, they are considered overweight or obese. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), an adult with a body mass index (BMI) between 25 and 29.9 is considered overweight (Figure 2). An adult with a BMI of 30 or higher is considered obese (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [CDC], 2012). People who are so overweight that they are at risk for death are classified as morbidly obese. Morbid obesity is defined as having a BMI over 40. Note that although BMI has been used as a healthy weight indicator by the World Health Organization (WHO), the CDC, and other groups, its value as an assessment tool has been questioned. The BMI is most useful for studying populations, which is the work of these organizations. It is less useful in assessing an individual since height and weight measurements fail to account for important factors like fitness level. An athlete, for example, may have a high BMI because the tool doesn’t distinguish between the body’s percentage of fat and muscle in a person’s weight.

Being extremely overweight or obese is a risk factor for several negative health consequences. These include, but are not limited to, an increased risk for cardiovascular disease, stroke, Type 2 diabetes, liver disease, sleep apnea, colon cancer, breast cancer, infertility, and arthritis. Given that it is estimated that in the United States around one-third of the adult population is obese and that nearly two-thirds of adults and one in six children qualify as overweight (CDC, 2012), there is substantial interest in trying to understand how to combat this important public health concern.
What causes someone to be overweight or obese? You have already read that both genes and environment are important factors for determining body weight, and if more calories are consumed than expended, excess energy is stored as fat. However, socioeconomic status and the physical environment must also be considered as contributing factors (CDC, 2012). For example, an individual who lives in an impoverished neighborhood that is overrun with crime may never feel comfortable walking or biking to work or to the local market. This might limit the amount of physical activity in which he engages and result in an increased body weight. Similarly, some people may not be able to afford healthy food options from their market, or these options may be unavailable (especially in urban areas or poorer neighborhoods); therefore, some people rely primarily on available, inexpensive, high fat, and high calorie fast food as their primary source of nutrition.
Generally, overweight and obese individuals are encouraged to try to reduce their weights through a combination of both diet and exercise. While some people are very successful with these approaches, many struggle to lose excess weight. In cases in which a person has had no success with repeated attempts to reduce weight or is at risk for death because of obesity, bariatric surgery may be recommended. Bariatric surgery is a type of surgery specifically aimed at weight reduction, and it involves modifying the gastrointestinal system to reduce the amount of food that can be eaten and/or limiting how much of the digested food can be absorbed (Figure 3) (Mayo Clinic, 2013). A recent meta-analysis suggests that bariatric surgery is more effective than non-surgical treatment for obesity in the two-years immediately following the procedure, but to date, no long-term studies yet exist (Gloy et al., 2013).

Dig Deeper: Prader-Willi Syndrome
Prader-Willi Syndrome (PWS) is a genetic disorder that results in persistent feelings of intense hunger and reduced rates of metabolism. Typically, affected children have to be supervised around the clock to ensure that they do not engage in excessive eating. Currently, PWS is the leading genetic cause of morbid obesity in children, and it is associated with a number of cognitive deficits and emotional problems (Figure 4).

While genetic testing can be used to make a diagnosis, there are a number of behavioral diagnostic criteria associated with PWS. From birth to 2 years of age, lack of muscle tone and poor sucking behavior may serve as early signs of PWS. Developmental delays are seen between the ages of 6 and 12, and excessive eating and cognitive deficits associated with PWS usually onset a little later.
While the exact mechanisms of PWS are not fully understood, there is evidence that affected individuals have hypothalamic abnormalities. This is not surprising, given the hypothalamus’s role in regulating hunger and eating. However, as you will learn in the next section of this module, the hypothalamus is also involved in the regulation of sexual behavior. Consequently, many individuals suffering from PWS fail to reach sexual maturity during adolescence.
There is no current treatment or cure for PWS. However, if weight can be controlled in these individuals, then their life expectancies are significantly increased (historically, sufferers of PWS often died in adolescence or early adulthood). Advances in the use of various psychoactive medications and growth hormones continue to enhance the quality of life for individuals with PWS (Cassidy & Driscoll, 2009; Prader-Willi Syndrome Association, 2012).
What you’ll learn to do: describe sexual behavior and research about sexuality
Learning Objectives
- Understand basic biological mechanisms regulating sexual behavior and motivation
- Explain the contributions of Alfred Kinsey’s and William Masters and Virginia Johnson’s research made to our understanding of sexual behavior
- Describe variations sexual orientation and gender identity
“Human sexuality” refers to people’s sexual interest in and attraction to others; it is the capacity to have erotic or sexual feelings and experiences. Sexuality differs from biological sex, in that “sexuality” refers to the capacity for sexual feelings and attraction, while “biological sex” refers to how one’s anatomy, physiology, hormones, and genetics are classified (typically as male, female, or intersex). Sexuality is also separate from gender identity, which is a person’s sense of their own gender, or sociocultural classification (i.e., man, woman, or another gender) based on biological sex (i.e., male or female). It is also distinct from—although it shapes—sexual orientation, or one’s emotional and sexual attraction to a particular sex or gender.
Sexuality may be experienced and expressed in a variety of ways, including thoughts, fantasies, desires, beliefs, attitudes, values, behaviors, practices, roles, and relationships. These manifest themselves not only in biological, physical, and emotional ways, but also in sociocultural ways, which have to do with the effects of human society and culture on one’s sexuality. Some researchers believe that sexual behavior is determined by genetics; however, others assert that it is largely molded by the environment. Human sexuality impacts, and is impacted by, cultural, political, legal, and philosophical aspects of life, and can interact with issues of morality, ethics, theology, spirituality, or religion.

Like food, sex is an important part of our lives. From an evolutionary perspective, the reason is obvious—perpetuation of the species. Sexual behavior in humans, however, involves much more than reproduction. This section provides an overview of research that has been conducted on human sexual behavior and motivation. This section will close with a discussion of issues related to gender and sexual orientation.
Physiological Mechanisms of Sexual Behavior and Motivation
Much of what we know about the physiological mechanisms that underlie sexual behavior and motivation comes from animal research. As you’ve learned, the hypothalamus plays an important role in motivated behaviors, and sex is no exception. In fact, lesions to an area of the hypothalamus called the medial preoptic area completely disrupt a male rat’s ability to engage in sexual behavior. Surprisingly, medial preoptic lesions do not change how hard a male rat is willing to work to gain access to a sexually receptive female (Figure 1). This suggests that the ability to engage in sexual behavior and the motivation to do so may be mediated by neural systems distinct from one another.
Animal research suggests that limbic system structures such as the amygdala and nucleus accumbens are especially important for sexual motivation. Damage to these areas results in a decreased motivation to engage in sexual behavior, while leaving the ability to do so intact (Figure 2) (Everett, 1990). Similar dissociations of sexual motivation and sexual ability have also been observed in the female rat (Becker, Rudick, & Jenkins, 2001; Jenkins & Becker, 2001).

Although human sexual behavior is much more complex than that seen in rats, some parallels between animals and humans can be drawn from this research. The worldwide popularity of drugs used to treat erectile dysfunction (Conrad, 2005) speaks to the fact that sexual motivation and the ability to engage in sexual behavior can also be dissociated in humans. Moreover, disorders that involve abnormal hypothalamic function are often associated with hypogonadism (reduced function of the gonads) and reduced sexual function (e.g., Prader-Willi syndrome). Given the hypothalamus’s role in endocrine function, it is not surprising that hormones secreted by the endocrine system also play important roles in sexual motivation and behavior. For example, many animals show no sign of sexual motivation in the absence of the appropriate combination of sex hormones from their gonads. While this is not the case for humans, there is considerable evidence that sexual motivation for both men and women varies as a function of circulating testosterone levels (Bhasin, Enzlin, Coviello, & Basson, 2007; Carter, 1992; Sherwin, 1988).
Kinsey’s Research
Before the late 1940s, access to reliable, empirically-based information on sex was limited. Physicians were considered authorities on all issues related to sex, despite the fact that they had little to no training in these issues, and it is likely that most of what people knew about sex had been learned either through their own experiences or by talking with their peers. Convinced that people would benefit from a more open dialogue on issues related to human sexuality, Dr. Alfred Kinsey of Indiana University initiated large-scale survey research on the topic (Figure 3). The results of some of these efforts were published in two books—Sexual Behavior in the Human Male and Sexual Behavior in the Human Female—which were published in 1948 and 1953, respectively (Bullough, 1998).

At the time, the Kinsey reports were quite sensational. Never before had the American public seen its private sexual behavior become the focus of scientific scrutiny on such a large scale. The books, which were filled with statistics and scientific lingo, sold remarkably well to the general public, and people began to engage in open conversations about human sexuality. As you might imagine, not everyone was happy that this information was being published. In fact, these books were banned in some countries. Ultimately, the controversy resulted in Kinsey losing funding that he had secured from the Rockefeller Foundation to continue his research efforts (Bancroft, 2004).
Although Kinsey’s research has been widely criticized as being riddled with sampling and statistical errors (Jenkins, 2010), there is little doubt that this research was very influential in shaping future research on human sexual behavior and motivation. Kinsey described a remarkably diverse range of sexual behaviors and experiences reported by the volunteers participating in his research. Behaviors that had once been considered exceedingly rare or problematic were demonstrated to be much more common and innocuous than previously imagined (Bancroft, 2004; Bullough, 1998).
Link to Learning
Watch this trailer from the 2004 film Kinsey that depicts Alfred Kinsey’s life and research.
Among the results of Kinsey’s research were the findings that women are as interested and experienced in sex as their male counterparts, that both males and females masturbate without adverse health consequences, and that homosexual acts are fairly common (Bancroft, 2004). Kinsey also developed a continuum known as the Kinsey scale that is still commonly used today to categorize an individual’s sexual orientation (Jenkins, 2010).
Masters and Johnson’s Research
In 1966, William Masters and Virginia Johnson published a book detailing the results of their observations of nearly 700 people who agreed to participate in their study of physiological responses during sexual behavior. Unlike Kinsey, who used personal interviews and surveys to collect data, Masters and Johnson observed people having intercourse in a variety of positions, and they observed people masturbating, manually or with the aid of a device. While this was occurring, researchers recorded measurements of physiological variables, such as blood pressure and respiration rate, as well as measurements of sexual arousal, such as vaginal lubrication and penile tumescence (swelling associated with an erection). In total, Masters and Johnson observed nearly 10,000 sexual acts as a part of their research (Hock, 2008).
Based on these observations, Masters and Johnson divided the sexual response cycle into four phases that are fairly similar in men and women: excitement, plateau, orgasm, and resolution (Figure 4). The excitement phase is the arousal phase of the sexual response cycle, and it is marked by erection of the penis or clitoris and lubrication and expansion of the vaginal canal. During plateau, women experience further swelling of the vagina and increased blood flow to the labia minora, and men experience full erection and often exhibit pre-ejaculatory fluid. Both men and women experience increases in muscle tone during this time. Orgasm is marked in women by rhythmic contractions of the pelvis and uterus along with increased muscle tension. In men, pelvic contractions are accompanied by a buildup of seminal fluid near the urethra that is ultimately forced out by contractions of genital muscles, (i.e., ejaculation). Resolution is the relatively rapid return to an unaroused state accompanied by a decrease in blood pressure and muscular relaxation. While many women can quickly repeat the sexual response cycle, men must pass through a longer refractory period as part of resolution. The refractory period is a period of time that follows an orgasm during which an individual is incapable of experiencing another orgasm. In men, the duration of the refractory period can vary dramatically from individual to individual with some refractory periods as short as several minutes and others as long as a day. As men age, their refractory periods tend to span longer periods of time.

In addition to the insights that their research provided with regards to the sexual response cycle and the multi-orgasmic potential of women, Masters and Johnson also collected important information about reproductive anatomy. Their research demonstrated the oft-cited statistic of the average size of a flaccid and an erect penis (3 and 6 inches, respectively) as well as dispelling long-held beliefs about relationships between the size of a man’s erect penis and his ability to provide sexual pleasure to his female partner. Furthermore, they determined that the vagina is a very elastic structure that can conform to penises of various sizes (Hock, 2008).
Link to Learning
Watch the following episode of Crash Course Psychology in which Hank talks about Kinsey, Masters and Johnson, sexuality, gender identity, hormones, and even looks into the idea of why people have sex.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=Qymp_VaFo9M%3Flist%3DPL8dPuuaLjXtOPRKzVLY0jJY-uHOH9KVU6
Sexual Orientation
A person’s sexual orientation is their emotional and erotic attraction toward another individual (Figure 1). While the majority of people identify as heterosexual (attraction to opposite-sexed individuals), there is a sizable population of people within the United States who identify as either homosexual (same-sex attraction) or bisexual (attraction to both sexes). Research suggests that somewhere between 3% and 10% of the population identifies as homosexual (Kinsey, Pomeroy, & Martin, 1948; LeVay, 1996; Pillard & Bailey, 1995).

Issues of sexual orientation have long fascinated scientists interested in determining what causes one individual to be heterosexual while another is homosexual. For many years, people believed that these differences arose because of different socialization and familial experiences. However, research has consistently demonstrated that the family backgrounds and experiences are very similar among heterosexuals and homosexuals (Bell, Weinberg, & Hammersmith, 1981; Ross & Arrindell, 1988).
Genetic and biological mechanisms have also been proposed, and the balance of research evidence suggests that sexual orientation has an underlying biological component. For instance, over the past 25 years, research has demonstrated gene-level contributions to sexual orientation (Bailey & Pillard, 1991; Hamer, Hu, Magnuson, Hu, & Pattatucci, 1993; Rodriguez-Larralde & Paradisi, 2009), with some researchers estimating that genes account for at least half of the variability seen in human sexual orientation (Pillard & Bailey, 1998). Other studies report differences in brain structure and function between heterosexuals and homosexuals (Allen & Gorski, 1992; Byne et al., 2001; Hu et al., 2008; LeVay, 1991; Ponseti et al., 2006; Rahman & Wilson, 2003a; Swaab & Hofman, 1990), and even differences in basic body structure and function have been observed (Hall & Kimura, 1994; Lippa, 2003; Loehlin & McFadden, 2003; McFadden & Champlin, 2000; McFadden & Pasanen, 1998; Rahman & Wilson, 2003b). In aggregate, the data suggest that to a significant extent, sexual orientations are something with which we are born.
Misunderstandings about Sexual Orientation
Regardless of how sexual orientation is determined, research has made clear that sexual orientation is not a choice, but rather it is a relatively stable characteristic of a person that cannot be changed. Claims of successful gay conversion therapy have received wide criticism from the research community due to significant concerns with research design, recruitment of experimental participants, and interpretation of data. As such, there is no credible scientific evidence to suggest that individuals can change their sexual orientation (Jenkins, 2010).
Dr. Robert Spitzer, the author of one of the most widely-cited examples of successful conversion therapy, apologized to both the scientific community and the gay community for his mistakes, and he publically recanted his own paper in a public letter addressed to the editor of Archives of Sexual Behavior in the spring of 2012 (Carey, 2012). In this letter, Spitzer wrote,
I was considering writing something that would acknowledge that I now judge the major critiques of the study as largely correct. . . . I believe I owe the gay community an apology for my study making unproven claims of the efficacy of reparative therapy. I also apologize to any gay person who wasted time or energy undergoing some form of reparative therapy because they believed that I had proven that reparative therapy works with some “highly motivated” individuals. (Becker, 2012, pars. 2, 5)
Citing research that suggests not only that gay conversion therapy is ineffective, but also potentially harmful, legislative efforts to make such therapy illegal have either been enacted (e.g., it is now illegal in California) or are underway across the United States, and many professional organizations have issued statements against this practice (Human Rights Campaign, n.d.)
Link to Learning
Read this draft of Dr. Spitzer’s letter.
Gender Identity
Many people conflate sexual orientation with gender identity because of stereotypical attitudes that exist about homosexuality. In reality, these are two related, but different, issues. Gender identity refers to one’s sense of being male or female. Generally, our gender identities correspond to our chromosomal and phenotypic sex, but this is not always the case. When individuals do not feel comfortable identifying with the gender associated with their biological sex, then they experience gender dysphoria. Gender dysphoria is a diagnostic category in the fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) that describes individuals who do not identify as the gender that most people would assume they are. This dysphoria must persist for at least six months and result in significant distress or dysfunction to meet DSM-5 diagnostic criteria. In order for children to be assigned this diagnostic category, they must verbalize their desire to become the other gender.
Cisgender is an umbrella terms used to describe people whose sense of personal identity and gender corresponds with their birth sex, while transgender is a term used to describe people whose sense of personal identity does not correspond with their birth sex. Approximately 1.4 million U.S. adults or .6 percent of the population are transgender according to a 2016 report.[1]
Many people who are classified as gender dysphoric seek to live their lives in ways that are consistent with their own gender identity. This involves dressing in opposite-sex clothing and assuming an opposite-sex identity. These individuals may also undertake transgender hormone therapy in an attempt to make their bodies look more like the opposite sex, and in some cases, they elect to have surgeries to alter the appearance of their external genitalia to resemble that of their gender identity (Figure 6). Transgender people who attempt to alter their bodies through medical interventions such as surgery and hormonal therapy are called transsexual individuals. They may also be known as male-to-female (MTF) or female-to-male (FTM). Not all transgender individuals choose to alter their bodies: many will maintain their original anatomy but may present themselves to society as another gender.

Link to Learning
Hear firsthand about the transgender experience and the disconnect that occurs when one’s self-identity is betrayed by one’s body.In this brief video interview, Chaz Bono discusses the difficulties of growing up identifying as male, while living in a female body.
Cultural Factors in Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity
Gender is deeply cultural. Like race, it is a social construction with real consequences, particularly for those who do not conform to gender binaries. In order to describe gender as a concept, we need to expand the language we use to describe gender beyond “masculine” or “feminine.” Gender identity, or the way that one thinks about gender and self-identifies, can be woman, man, or genderqueer.
Gender expression, or how one demonstrates gender (based on traditional gender role norms related to clothing, behavior, and interactions) can be feminine, masculine, androgynous, or somewhere along a spectrum. Although gender has traditionally been considered in binary terms (male or female), increasingly gender is being seen as a spectrum; however, our vocabulary is still limited in terms of the ways in which we describe gender identity.
Issues related to sexual orientation and gender identity are very much influenced by sociocultural factors. Even the ways in which we define sexual orientation and gender vary from one culture to the next. While in the United States exclusive heterosexuality is viewed as the norm, there are societies that have different attitudes regarding homosexual behavior. In fact, in some instances, periods of exclusively homosexual behavior are socially prescribed as a part of normal development and maturation. For example, in parts of New Guinea, young boys are expected to engage in sexual behavior with other boys for a given period of time because it is believed that doing so is necessary for these boys to become men (Baldwin & Baldwin, 1989).
There is a two-gendered culture in the United States. We tend to classify an individual as either male or female. However, in some cultures there are additional gender variants resulting in more than two gender categories. For example, in Thailand, you can be male, female, or kathoey. A kathoey is an individual who would be described as intersexed or transgender in the United States (Tangmunkongvorakul, Banwell, Carmichael, Utomo, & Sleigh, 2010).
Dig Deeper: The Case of David Reimer
In August of 1965, Janet and Ronald Reimer of Winnipeg, Canada, welcomed the birth of their twin sons, Bruce and Brian. Within a few months, the twins were experiencing urinary problems; doctors recommended the problems could be alleviated by having the boys circumcised. A malfunction of the medical equipment used to perform the circumcision resulted in Bruce’s penis being irreparably damaged. Distraught, Janet and Ronald looked to expert advice on what to do with their baby boy. By happenstance, the couple became aware of Dr. John Money at Johns Hopkins University and his theory of psychosexual neutrality (Colapinto, 2000).
Dr. Money had spent a considerable amount of time researching transgender individuals and individuals born with ambiguous genitalia. As a result of this work, he developed a theory of psychosexual neutrality. His theory asserted that we are essentially neutral at birth with regard to our gender identity and that we don’t assume a concrete gender identity until we begin to master language. Furthermore, Dr. Money believed that the way in which we are socialized in early life is ultimately much more important than our biology in determining our gender identity (Money, 1962).
Dr. Money encouraged Janet and Ronald to bring the twins to Johns Hopkins University, and he convinced them that they should raise Bruce as a girl. Left with few other options at the time, Janet and Ronald agreed to have Bruce’s testicles removed and to raise him as a girl. When they returned home to Canada, they brought with them Brian and his “sister,” Brenda, along with specific instructions to never reveal to Brenda that she had been born a boy (Colapinto, 2000).
Early on, Dr. Money shared with the scientific community the great success of this natural experiment that seemed to fully support his theory of psychosexual neutrality (Money, 1975). Indeed, in early interviews with the children it appeared that Brenda was a typical little girl who liked to play with “girly” toys and do “girly” things.
However, Dr. Money was less than forthcoming with information that seemed to argue against the success of the case. In reality, Brenda’s parents were constantly concerned that their little girl wasn’t really behaving as most girls did, and by the time Brenda was nearing adolescence, it was painfully obvious to the family that she was really having a hard time identifying as a female. In addition, Brenda was becoming increasingly reluctant to continue her visits with Dr. Money to the point that she threatened suicide if her parents made her go back to see him again.
At that point, Janet and Ronald disclosed the true nature of Brenda’s early childhood to their daughter. While initially shocked, Brenda reported that things made sense to her now, and ultimately, by the time she was an adolescent, Brenda had decided to identify as a male. Thus, she became David Reimer.
David was quite comfortable in his masculine role. He made new friends and began to think about his future. Although his castration had left him infertile, he still wanted to be a father. In 1990, David married a single mother and loved his new role as a husband and father. In 1997, David was made aware that Dr. Money was continuing to publicize his case as a success supporting his theory of psychosexual neutrality. This prompted David and his brother to go public with their experiences in attempt to discredit the doctor’s publications. While this revelation created a firestorm in the scientific community for Dr. Money, it also triggered a series of unfortunate events that ultimately led to David committing suicide in 2004 (O’Connell, 2004).
This sad story speaks to the complexities involved in gender identity. While the Reimer case had earlier been paraded as a hallmark of how socialization trumped biology in terms of gender identity, the truth of the story made the scientific and medical communities more cautious in dealing with cases that involve intersex children and how to deal with their unique circumstances. In fact, stories like this one have prompted measures to prevent unnecessary harm and suffering to children who might have issues with gender identity. For example, in 2013, a law took effect in Germany allowing parents of intersex children to classify their children as indeterminate so that children can self-assign the appropriate gender once they have fully developed their own gender identities (Paramaguru, 2013).
Link to Learning
Watch this news story about the experiences of David Reimer and his family.
Putting It Together: Motivation and Emotion
Learning Objectives
In this chapter, you learned to
- explain motivation, how it is influenced, and major theories about motivation
- explain theories of emotion and how we express and recognize emotion
- explain feeding and sexual motivations
In this chapter, you learned about emotion and motivation. Understanding cultural similarities and differences in emotion is obviously critical to understanding emotions in general, and the flexibility of emotional processes more specifically. Given the central role that emotions play in our interaction, understanding cultural similarities and differences is especially critical to preventing potentially harmful miscommunications. Although misunderstandings are unintentional, they can result in negative consequences—as we’ve seen historically for ethnic minorities in many cultures. For instance, across a variety of North American settings, Asian Americans are often characterized as too “quiet” and “reserved,” and these low arousal states are often misinterpreted as expressions of disengagement or boredom—rather than expressions of the ideal of calmness. Consequently, Asian Americans may be perceived as “cold,” “stoic,” and “unfriendly,” fostering stereotypes of Asian Americans as “perpetual foreigners” (Cheryan & Monin, 2005). Indeed, this may be one reason Asian Americans are often overlooked for top leadership positions (Hyun, 2005).
In addition to averting cultural miscommunications, recognizing cultural similarities and differences in emotion may provide insights into other paths to psychological health and well-being. For instance, findings from a recent series of studies suggest that calm states are easier to elicit than excited states, suggesting that one way of increasing happiness in cultures that value excitement may be to increase the value placed on calm states (Chim, Tsai, Hogan, & Fung, 2013).
Based on studies comparing North American and East Asian contexts, there is clear evidence for cultural similarities and differences in emotions, and most of the differences can be traced to different cultural models of the self.
Consider your own concept of self for a moment. What kinds of pastimes do you prefer—activities that make you excited, or ones that make you calm? What kinds of feelings do you strive for? What is your ideal affect? Because emotions seem and feel so instinctual to us, it’s hard to imagine that the way we experience them and the ones we desire are anything other than biologically programmed into us. However, as current research has shown (and as future research will continue to explore), there are myriad ways in which culture, both consciously and unconsciously, shapes people’s emotional lives.
Chapter References (Click to expand)
Baldwin, J. D., & Baldwin, J. I. (1989). The socialization of homosexuality and heterosexuality in a non-western society. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 18, 13–29.
Bandura, A. (1994). Self-efficacy. In V. S. Ramachandran (Ed.), Encyclopedia of human behavior (Vol. 4, pp. 71–81). New York, NY: Academic Press.
Bauminger, N. (2002). The facilitation of social-emotional understanding and social interaction in high-functioning children with autism: Intervention outcomes. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 32, 283–298.
Beedie, C. J., Terry, P. C., Lane, A. M., & Devonport, T. J. (2011). Differential assessment of emotions and moods: Development and validation of the emotion and mood components of anxiety questionnaire. Personality and Individual Differences, 50, 228–233.
Berlyne, D. E. (1960). Toward a theory of exploratory behavior: II. Arousal potential, perceptual curiosity, and learning. In (Series Ed.), Conflict, arousal, and curiosity (pp. 193–227). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Book Company.
Blackford, J. U., & Pine, D. S. (2012). Neural substrates of childhood anxiety disorders: A review of neuroimaging findings. Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics of North America, 21, 501–525.
Bremner, J. D., & Vermetten, E. (2004). Neuroanatomical changes associated with pharmacotherapy in posttraumatic stress disorder. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1032, 154–157.
Buck, R. (1980). Nonverbal behavior and the theory of emotion: The facial feedback hypothesis. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 38, 811–824.
Bylsma, L., Morris, B., & Rottenberg, J. (2008). A meta-analysis of emotional reactivity in major depressive disorder. Clinical Psychology Review, 28(4), 676–691.
Cameron, J., & Pierce, W. D. (1994). Reinforcement, reward, and intrinsic motivation: A meta-analysis. Review of Educational Research, 64, 363–423.
Chentsova-Dutton, Y. E., Chu, J. P., Tsai, J. L., Rottenberg, J., Gross, J. J., & Gotlib, I. H. (2007). Depression and emotional reactivity: Variation among Asian Americans of East Asian descent and European Americans. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 116(4), 776–785.
Chentsova-Dutton, Y. E., Tsai, J. L., & Gotlib, I. (2010). Further evidence for the cultural norm hypothesis: Positive emotion in depressed and control European American and Asian American women. Cultural Diversity and Ethnic Minority Psychology, 16, 284–295.
Cheryan, S., & Monin, B. (2005). Where are you really from?: Asian Americans and identity denial. Journal of personality and social psychology, 89(5), 717–731.
Chim, L., Moon, A., Ang, J., & Tsai, J. L. (2013). Magazine ads, Facebook pages, and company websites reflect cultural differences in ideal affect. In T. Masuda (Chair). Culture and mind: Implications for art, design, and advertising. Symposium held at International Association for Cross-Cultural Psychology, Los Angeles, CA.
Chim, L., Tsai, J.L., Hogan, C., & Fung, H. H. (2013). Enhancing happiness by valuing calm. Manuscript in preparation.
Chwalisz, K., Diener, E., & Gallagher, D. (1988). Autonomic arousal feedback and emotional experience: Evidence from the spinal cord injured. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 54, 820–828.
Cousins, S. D. (1989). Culture and self-perception in Japan and the United States. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 56(1), 124–131.
Cunha, C., Monfils, M. H., & LeDoux, J. E. (2010). GABA(C) receptors in the lateral amygdala: A possible novel target for the treatment of fear and anxiety disorders? Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 4, 6.
Curhan, K., Sims, T., Markus, H., Kitayama, S., Karasawa, M., Kawakami, N., . . . Ryff, C. (2013). Negative affect predicts worse physical and mental health in the U.S. than in Japan. Manuscript under review.
Daniel, T. L., & Esser, J. K. (1980). Intrinsic motivation as influenced by rewards, task interest, and task structure. Journal of Applied Psychology, 65, 566–573.
Darwin, C. (1872). The expression of emotions in man and animals. New York, NY: Appleton.
Davis, J. I., Senghas, A., & Ochsner, K. N. (2009). How does facial feedback modulate emotional experience? Journal of Research in Personality, 43, 822–829.
Deci, E. L. (1972). Intrinsic motivation, extrinsic reinforcement, and inequity. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 22, 113–120.
Deci, E. L., Koestner, R., & Ryan, R. M. (1999). A meta-analytic review of experiments examining the effects of extrinsic rewards on intrinsic motivation. Psychological Bulletin, 125, 627–668.
de Gelder, B. (2006). Towards the neurobiology of emotional body language. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 7, 242–249.
Ekman, P., & Keltner, D. (1997). Universal facial expressions of emotion: An old controversy and new findings. In U. Segerstråle & P. Molnár (Eds.), Nonverbal communication: Where nature meets culture (pp. 27–46). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Femenía, T., Gómez-Galán, M., Lindskog, M., & Magara, S. (2012). Dysfunctional hippocampal activity affects emotion and cognition in mood disorders. Brain Research, 1476, 58–70.
Faris, E. (1921). Are instincts data or hypotheses? American Journal of Sociology, 27, 184–196.
Fossati, P. (2012). Neural correlates of emotion processing: From emotional to social brain. European Neuropsychopharmacology, 22, S487–S491.
Fournier, J. C., Keener, M. T., Almeida, J., Kronhaus, D. M., & Phillips, M. L. (2013). Amygdala and whole-brain activity to emotional faces distinguishes major depressive disorder and bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disorders. Advance online publication. doi:10.1111/bdi.12106
Francis, N. H., & Kritsonis, W. A. (2006). A brief analysis of Abraham Maslow’s original writing of Self-Actualizing People: A Study of Psychological Health. Doctoral Forum National Journal of Publishing and Mentoring Doctoral Student Research, 3, 1–7.
Freud, S. (1910). Five lectures on psycho-analysis. (Vol. XI). London: Hogarth Press.
Golan, O., & Baron-Cohen, S. (2006). Systemizing empathy: Teaching adults with Asperger syndrome or high-functioning autism to recognize complex emotions using interactive multimedia. Development and Psychopathology, 18, 591–617.
Goosens, K. A., & Maren, S. (2002). Long-term potentiation as a substrate for memory: Evidence from studies of amygdaloid plasticity and Pavlovian fear conditioning. Hippocampus, 12, 592–599.
Graham, S., & Weiner, B. (1996). Theories and principles of motivation. In D. C. Berliner & R. C. Calfee (Eds.), Handbook of educational psychology (pp. 63–84). New York, NY: Routledge.
Gross, J. J. (1998). Antecedent- and response-focused emotion regulation: Divergent consequences for experience, expression, and physiology. Journal of personality and social psychology, 74(1), 224–237.
Guastella, A. J., Einfeld, S. L., Gray, K. M., Rinehart, N. J., Tonge, B. J., Lambert, T. J., & Hickie, I. B. (2010). Intranasal oxytocin improves emotion recognition for youth with autism spectrum disorders. Biological Psychiatry, 67, 692–694.
Havas, D. A., Glenberg, A. M., Gutowski, K. A., Lucarelli, M. J., & Davidson, R. J. (2010). Cosmetic use of botulinum toxin-A affects processing of emotional language. Psychological Science, 21, 895–900.
Heine, S., Lehman, D., Markus, H., & Kitayama, S. (1999). Is there a universal need for positive self-regard? Psychological Review, 106(4), 766–794.
Hobson, R. P. (1986). The autistic child’s appraisal of expressions of emotion. The Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 27, 321–342.
Hofstede, G. (2001). Culture\'s Consequences: comparing values, behaviors, institutions, and organizations across nations (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications.
Hyun, J. (2005). Breaking the bamboo ceiling: Career strategies for Asians. New York. Harper Collins.
Koltko-Rivera, M. E. (2006). Rediscovering the later version of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs: Self-transcendence and opportunities for theory, research, and unification. Review of General Psychology, 10, 302–317.
Kwan, V., Bond, M., & Singelis, T. (1997). Pancultural explanations for life satisfaction: Adding relationship harmony to self-esteem. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 73(5), 1038–1051.
Lang, P. J. (1994). The varieties of emotional experience: A meditation on James-Lange theory. Psychological Review, 101, 211–221.
Lazarus, R. S. (1991). Emotion and adaptation. New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
LeDoux, J. E. (1996). The Emotional Brain: The Mysterious Underpinnings of Emotional Life. New York, NY: Simon & Schuster.
LeDoux, J. E. (2002). The synaptic self. London, UK: Macmillan.
Leonard, G. (1982). The failure of self-actualization theory: A critique of Carl Rogers and Abraham Maslow. Journal of Humanistic Psychology, 22, 56–73.
Levy-Gigi, E., Szabó, C., Kelemen, O., & Kéri, S. (2013). Association among clinical response, hippocampal volume, and FKBP5 gene expression in individuals with posttraumatic stress disorder receiving cognitive behavioral therapy. Biological Psychiatry, 74, 793–800.
Macdonald, H., Rutter, M., Howlin, P., Rios, P., Conteur, A. L., Evered, C., & Folstein, S. (1989). Recognition and expression of emotional cues by autistic and normal adults. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 30, 865–877.
Malatesta, C. Z., & Haviland, J. M. (1982). Learning display rules: The socialization of emotion expression in infancy. Child Development, 53, 991–1003.
Maren, S., Phan, K. L., & Liberzon, I. (2013). The contextual brain: Implications for fear conditioning, extinction and psychopathology. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 14, 417–428.
Markus, H., & Kitayama, S. (1991). Culture and the self: Implications for cognition, emotion, and motivation. Psychological Review, 98(2), 224–253. doi: 10.1037/0033-295X.98.2.224
Maslow, A. H. (1943). A theory of human motivation. Psychological Review, 50, 370–396.
Matsumoto, D. (1990). Cultural similarities and differences in display rules. Motivation and Emotion, 14, 195–214.
Matsumoto, D., Yoo, S. H., & Nakagawa, S. (2008). Culture, emotion regulation, and adjustment. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 94, 925–937.
McAdams, D. P., & Constantian, C. A. (1983). Intimacy and affiliation motives in daily living: An experience sampling analysis. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 45, 851–861.
McClelland, D. C., & Liberman, A. M. (1949). The effect of need for achievement on recognition of need-related words. Journal of Personality, 18, 236–251.
McRae, K., Ochsner, K. N., Mauss, I. B., Gabrieli, J. J. D., & Gross, J. J. (2008). Gender differences in emotion regulation: An fMRI study of cognitive reappraisal. Group Processes and Intergroup Relations, 11, 143–162.
Miguel-Hidalgo, J. J. (2013). Brain structural and functional changes in adolescents with psychiatric disorders. International Journal of Adolescent Medicine and Health, 25, 245–256.
Miyamoto, Y., Uchida, Y., & Ellsworth, P. C. (2010). Culture and mixed emotions: Co-occurrence of positive and negative emotions in Japan and the United States. Emotion, 10(3), 404–415. doi: 10.1037/a0018430
Moriceau, S., & Sullivan, R. M. (2006). Maternal presence serves as a switch between learning fear and attraction in infancy. Nature Neuroscience, 9, 1004–1006.
Morling, B., Kitayama, S., & Miyamoto, Y. (2002). Cultural practices emphasize influence in the United States and adjustment in Japan. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 28, 311–323.
Murray, H. A., Barrett, W. G., Homburger, E., Langer, W. C., Mekeel, H. S., Morgan, C. D., . . . Wolf, R. E. (1938). Explorations in personality: A clinical and experimental study of fifty men of college age. New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Niemiec, C. P., & Ryan, R. M. (2009). Autonomy, competence, and relatedness in the classroom: Applying self-determination theory to educational practice. Theory and Research in Education, 7, 133–144.
Oishi, S., Diener, E. F., Lucas, R. E., & Suh, E. M. (1999). Cross-cultural variations in predictors of life satisfaction: Perspectives from needs and values. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 25(8), 980–990.
Pessoa, L. (2010). Emotion and cognition and the amygdala: From “what is it?” to “what’s to be done?” Neuropsychologia, 48, 3416–3429.
Qin, S., Young, C. B., Duan, X., Chen, T., Supekar, K., & Menon, V. (2013). Amygdala subregional structure and intrinsic functional connectivity predicts individual differences in anxiety during early childhood. Biological Psychiatry. Advance online publication. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.10.006
Raineki, C., Cortés, M. R., Belnoue, L., & Sullivan, R. M. (2012). Effects of early-life abuse differ across development: Infant social behavior deficits are followed by adolescent depressive-like behaviors mediated by the amygdala. The Journal of Neuroscience, 32, 7758–7765.
Saxe, L., & Ben-Shakhar, G. (1999). Admissibility of polygraph tests: The application of scientific standards post-Daubert. Psychology, Public Policy, and Law, 5, 203–223.
Schachter, S., & Singer, J. E. (1962). Cognitive, social, and physiological determinants of emotional state. Psychological Review, 69, 379–399.
Sims, T., Tsai, J., Wang, I., Fung, H. H., & Zhang, X. L. (2013). Whether you experience the bad with the good depends on how you want to feel: Understanding cultural differences in the relationship between positive and negative affect. Manuscript in progress.
Soto, J., Perez, C., Kim, Y. H., Lee, E., & Minnick, M. (2011). Is expressive suppression always associated with poorer psychological functioning? A cross-cultural comparison between European Americans and Hong Kong Chinese. Emotion, 11(6), 1450–1455.
Soussignan, R. (2001). Duchenne smile, emotional experience, and autonomic reactivity: A test of the facial feedback hypothesis. Emotion, 2, 52–74.
Strack, F., Martin, L. & Stepper, S. (1988). Inhibiting and facilitating conditions of the human smile: A nonobtrusive test of the facial feedback hypothesis. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 54, 768–777.
Suh, E., Diener, E., Oishi, S., & Triandis, H. (1998). The shifting basis of life satisfaction judgments across cultures: Emotions versus norms. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 74(2), 482.
Tamietto, M., Castelli, L., Vighetti, S., Perozzo, P., Geminiani, G., Weiskrantz, L., & de Gelder, B. (2009). Unseen facial and bodily expressions trigger fast emotional reactions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,USA, 106, 17661–17666.
Tsai, J. L., Chentsova-Dutton, Y., Freire-Bebeau, L., & Przymus, D. (2002). Emotional expression and physiology in European Americans and Hmong Americans. Emotion, 2(4), 380–397. doi: 10.1037/1528-3542.2.4.380
Tsai, J. L., Levenson, R. W., & Carstensen, L. L. (2000). Autonomic, subjective, and expressive responses to emotional films in older and younger Chinese Americans and European Americans. Psychology and Aging, 15(4), 684–693.
Tsai, J. L., Levenson, R., & McCoy, K. (2006). Cultural and temperamental variation in emotional response. Emotion, 6(3), 484–497. doi: 10.1037/1528-3542.6.3.484
Tsai, J. L., Louie, J., Chen, E. E., & Uchida, Y. (2007). Learning what feelings to desire: Socialization of ideal affect through children’s storybooks. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 33, 17–30.
Tsai, J. L., Miao, F. F., Seppala, E., Fung, H. H., & Yeung, D. (2007). Influence and adjustment goals: Sources of cultural differences in ideal affect. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 92, 1102–1117.
Tsai, J. L., Sims, T., Thomas, E., & Fung, H. H. (2013). Ideal affect across the life span: A comparison of European American, Chinese American, and Hong Kong Chinese. Manuscript in progress.
Wang, Z., Neylan, T. C., Mueller, S. G., Lenoci, M., Truran, D., Marmar, C. R., . . . Schuff, N. (2010). Magnetic resonance imaging of hippocampal subfields in posttraumatic stress disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry, 67(3), 296–303. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2009.205
Weisz, J., Rothbaum, F., & Blackburn, T. (1984). Standing out and standing in: The psychology of control in American and Japan. American Psychologist, 39, 955–969.
Yerkes, R. M., & Dodson, J. D. (1908). The relation of strength of stimulus to rapidity of habit-formation. Journal of Comparative Neurology and Psychology, 18, 459–482. doi:10.1002/cne.920180503
Zajonc, R. B. (1980). Feeling and thinking: Preferences need no inferences. American Psychologist, 35(2), 151–175.
Zajonc, R. B. (1998). Emotions. In D. T. Gilbert & S. T. Fiske (Eds.), Handbook of social psychology (4th ed., Vol. 1, pp. 591–632). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Licenses and Attributions (Click to expand)
CC licensed content, Original
- Emotion and Motivation. Authored by: Karenna Malavanti Provided by: PressBooks. License: CC BY-SA-NC: Attribution-ShareALike-NonCommercial
CC licensed content, Shared previously
- Why It Matters: Emotion and Motivation. Authored by: Lumen Learning Provided by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution Located at: https://pressbooks.online.ucf.edu/lumenpsychology/chapter/introduction-7/
- Introduction to Emotion and Motivation. Authored by: OpenStax College. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Download for free at https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction. Located at: https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/10-introduction.
- Introduction to Motivation. Authored by: Lumen Learning Provided by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution Located at: https://pressbooks.online.ucf.edu/lumenpsychology/chapter/introduction-motivation/
- Motivation. Authored by: OpenStax College. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Download for free at https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction. Located at: https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/10-1-motivation.
- climbing picture. Provided by: Pixabay. License: CC0: No Rights Reserved. Located at: https://www.pexels.com/photo/achievement-action-adventure-backlit-209209/.
- Motivation. Authored by: Lumen Learning Provided by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution Located at: https://pressbooks.online.ucf.edu/lumenpsychology/chapter/motivation/
- Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs. Authored by: Lumen Learning Provided by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution Located at: https://pressbooks.online.ucf.edu/lumenpsychology/chapter/maslows-hierarchy-of-needs/
- Introduction to Emotion. Authored by: Lumen Learning Provided by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike Located at: https://pressbooks.online.ucf.edu/lumenpsychology/chapter/introduction-to-emotion/
- Describing Emotion. Provided by: Boundless. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike. Located at: https://www.boundless.com/psychology/textbooks/boundless-psychology-textbook/emotion-13/defining-emotion-503/defining-emotion-504-16761/.
- Emotion. Authored by: OpenStax College. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Download for free at https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction. Located at: https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/10-4-emotion.
- Portrait of a Man showing emotions. Authored by: Gert Germeraad. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike. Located at: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Portret_van_een_man005.jpg.
- Theories of Emotion. Authored by: Lumen Learning Provided by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution Located at: https://pressbooks.online.ucf.edu/lumenpsychology/chapter/emotion/
- The Biology of Emotions. Authored by: Lumen Learning Provided by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution Located at: https://pressbooks.online.ucf.edu/lumenpsychology/chapter/the-biology-of-emotions/
- Seeing Emotion. Authored by: Lumen Learning Provided by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution Located at: https://pressbooks.online.ucf.edu/lumenpsychology/chapter/seeing-emotion/
- Emotion interactive. Authored by: Jessica Traylor for Lumen Learning. Provided by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Hunger and Eating. Authored by: OpenStax College. Located at: https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/10-2-hunger-and-eating. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Download for free at https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Anorexia picture. Authored by: Benjamin Watson. Provided by: Flickr. Located at: https://www.flickr.com/photos/schnappischnap/8970182946. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Sexual Behavior objectives. Authored by: OpenStax College. Located at: https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/10-3-sexual-behavior. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Download for free at https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Human Sexuality and Culture. Provided by: Boundless. Project: Boundless Psychology. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: https://www.boundless.com/psychology/textbooks/boundless-psychology-textbook/gender-and-sexuality-15/sexuality-415/human-sexuality-and-culture-299-12834/
- picture. Provided by: freestocks.org. Located at: https://www.pexels.com/photo/adult-couple-dock-fashion-349494/. License: CC0: No Rights Reserved
- Let's Talk About Sex: Crash Course Psychology #27. Authored by: Hank Green. Provided by: CrashCourse. Located at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qymp_VaFo9M&feature=youtu.be&list=PL8dPuuaLjXtOPRKzVLY0jJY-uHOH9KVU6. License: Other. License Terms: Standard YouTube License
- Additional material on gender identity. Provided by: Lumen Learning. Located at: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/wm-introductiontosociology/chapter/sex-and-gender/. Project: Introduction to Sociology. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Example Video. Authored by: heirospace. Located at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TG-lR3uF6Ag. License: All Rights Reserved. License Terms: Standard YouTube License
- Transgender Migrants Seek Asylum in the US. Provided by: VOA News. Located at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qN78g2MpboE. License: All Rights Reserved. License Terms: Standard YouTube License
- Putting It Together: Motivation and Emotion. Authored by: Lumen Learning Provided by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution Located at: https://pressbooks.online.ucf.edu/lumenpsychology/chapter/putting-it-together-motivation-and-emotion/
All Rights Reserved Content
- Feeling All the Feels: Crash Course Psychology #25. Authored by: Hank Green. Provided by: CrashCourse. License: Other. License Terms: Standard YouTube License. Located at: https://youtu.be/gAMbkJk6gnE?t=2m2s.
- RSA ANIMATE: Drive: The surprising truth about what motivates us. Authored by: Dan Pink. Located at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u6XAPnuFjJc. License: Other. License Terms: Standard YouTube License
Public domain content
- Little boy playing with toy. Authored by: Staff Sgt. Ashley Hawkins. Provided by: U.S. Air Force. License: Public Domain: No Known Copyright Located at: http://www.jble.af.mil/News/Photos/igphoto/2000166395/.
- [footnote]Flores, A., J. Herman, G. Gates, and T. N.T. Brown. "How many adults identify as transgender." The Williams Institute. http://williamsinstitute.law.ucla.edu/wp-content/uploads/How-Many-Adults-Identify-as-Transgender-in-the-United-States.pdf. ↵
wants or needs that direct behavior toward some goal
motivation based on internal feelings rather than external rewards
motivation that arises from external factors or rewards
species-specific pattern of behavior that is unlearned
deviations from homeostasis create physiological needs that result in psychological drive states that direct behavior to meet the need and ultimately bring the system back to homeostasis
pattern of behavior in which we regularly engage
simple tasks are performed best when arousal levels are relatively high, while complex tasks are best performed when arousal is lower
individual’s belief in his own capabilities or capacities to complete a task
spectrum of needs ranging from basic biological needs to social needs to self-actualization
subjective state of being often described as feelings
physiological arousal, psychological appraisal, and subjective experience
emotions arise from physiological arousal
physiological arousal and emotional experience occur at the same time
facial expressions are capable of influencing our emotions
emotions consist of two factors: physiological and cognitive
lie detector test that measures physiological arousal of individuals as they answer a series of questions
our emotions are determined by our appraisal of the stimulus
structure in the limbic system involved in our experience of emotion and tying emotional meaning to our memories
part of the brain with dense connections with a variety of sensory areas of the brain; it is critical for classical conditioning and attaching emotional value to memory
part of the brain involved in attention and has connections with the hypothalamus and various brainstem areas to regulate the autonomic nervous and endocrine systems’ activity
structure in the temporal lobe associated with learning and memory
one of the culturally specific standards that govern the types and frequencies of emotions that are acceptable
emotional expression through body position or movement
type of eating disorder characterized by binge eating followed by purging
type of eating disorder characterized by binge eating and associated distress
eating disorder characterized by an individual maintaining body weight that is well below average through starvation and/or excessive exercise
individuals view themselves as overweight even though they are not
fullness; satisfaction
satiety hormone
amount of energy that is expended in a given period of time
assertion that each individual has an ideal body weight, or set point, that is resistant to change
adult with a BMI between 25 and 29.9
adult with a BMI of 30 or higher
adult with a BMI over 40
phase of the sexual response cycle that involves sexual arousal
phase of the sexual response cycle that falls between excitement and orgasm
peak phase of the sexual response cycle associated with rhythmic muscle contractions (and ejaculation)
phase of the sexual response cycle following orgasm during which the body returns to its unaroused state
time immediately following an orgasm during which an individual is incapable of experiencing another orgasm
emotional and erotic attraction to same-sexed individuals, opposite-sexed individuals, or both
emotional and erotic attractions to opposite-sexed individuals
emotional and erotic attractions to same-sexed individuals
emotional and erotic attractions to both same-sexed individuals and opposite-sexed individuals
individual’s sense of being male or female
assumes workers are people who seek to work hard and productively; managers and workers can find creative solutions to problems; workers do not need to be controlled and punished
an umbrella terms used to describe people whose sense of personal identity and gender corresponds with their birth sex
a term used to describe people whose sense of personal identity does not correspond with their birth sex
use of hormones to make one’s body look more like the opposite-sex
transgender individuals who attempt to alter their bodies through medical interventions such as surgery and hormonal therapy


